New release 2019/05/03
Polymer synthesis method of Polyacrylamide (MBam)
1. As acrylic acid (CH2 = CHCOOH) and acrylamide (CH2 = CHCONH2)
2. N, N’-Methylenebisacrylamide MBam ((CH2 = CHCONH)2CH2)
3. ABAP: 2,2-azobis (2-amidinopropane) hydrochloride (C8H18N6. 2HCl) as a polymerization initiator
4. acrylic acid (CH2 ═CHCOOH) and acrylamide (CH2 ═ CHCONH2) are blended in equal amounts and heated at 60 ° C. by overheating
5. Neutralize with KOH and cool
6. Melt by heating at 60 degrees and add ABAP (0.01% to 0.1% absorb large amount, cure as it approaches 0.2%)
7. Cooling
Polyacrylamide Gel
A Polyacrylamide Gel is a separation matrix used in electrophoresis of biomolecules, such as proteins or DNA fragments. Traditional DNA sequencing techniques such as Maxam-Gilbert or Sanger methods used polyacrylamide gels to separate DNA fragments differing by a single base-pair in length so the sequence could be read. Most modern DNA separation methods now use agarose gels, except for particularly small DNA fragments. It is currently most often used in the field of immunology and protein analysis, often used to separate different proteins or isoforms of the same protein into separate bands. These can be transferred onto a nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane to be probed with antibodies and corresponding markers, such as in a western blot. PAGE is the often-used acronym for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, where electrophoresis means applying an electric field to mediate the movement of particles through the polyacrylamide gel.
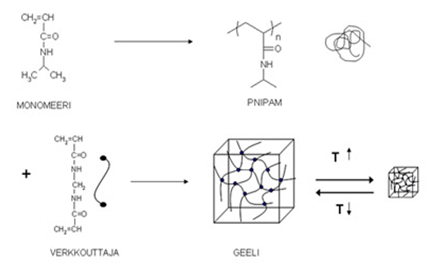
We are understand of choice at NATIVE PAGE method for Tissue Engineering process. This type is one of PAGE technology.
Attention
A corporate name, the brand name, and the design logo that has been described are the trademarks or registered trademarks of each company.
Biological Process System Technology Taiwan copyright(C)All rights reserved 2019